For strategic analysis and business strategy development, use the convenient visual tools presented in the game menu: My Company / Strategy.
Business Canvas Model
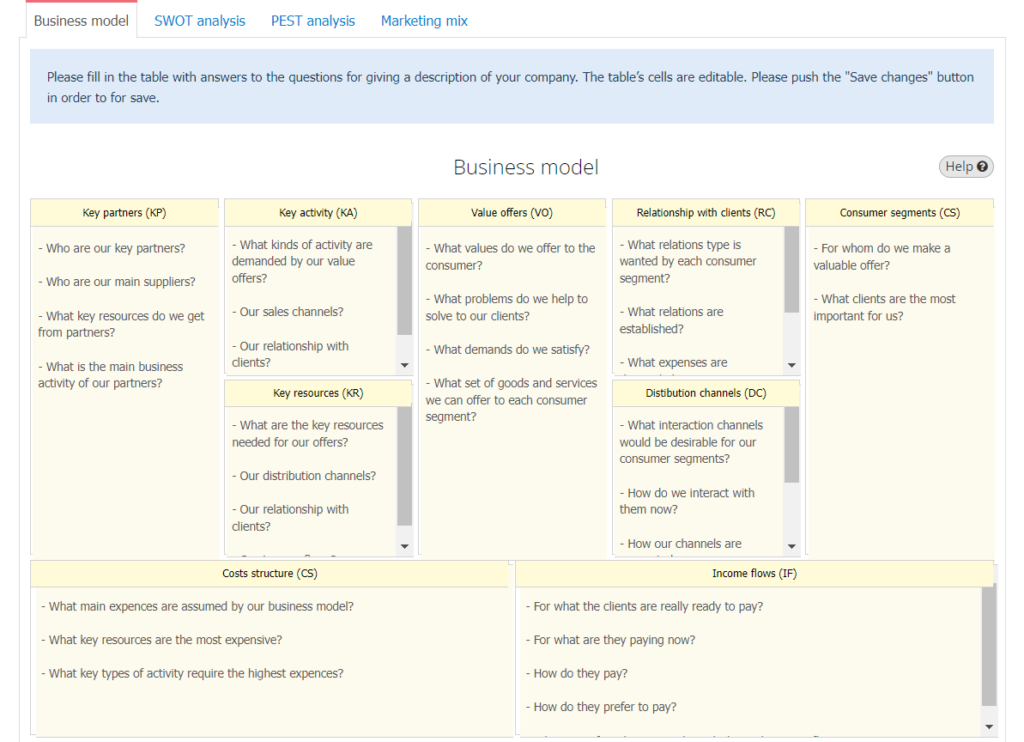
The Business Canvas Model is a strategic management tool that allows you to describe a project on one sheet of paper, analyze it, and find strengths and weaknesses. The method was invented and described by Swiss business analyst Alexander Osterwalder.
SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning and management technique to help a person or organization identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning. It is sometimes called situational assessment or situational analysis. This technique is designed for use in the preliminary stages of decision-making processes. It can be used as a tool for the evaluation of the strategic position of companies or products.

- Strengths: characteristics of the business or project that give it an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses: characteristics that place the business or project at a disadvantage relative to others.
- Opportunities: elements in the environment that the business or project could exploit to its advantage.
- Threats: elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project.
PEST analysis
PEST analysis (“political, economic, socio-cultural and technological”) describes a framework of macro-environmental factors used in the environmental scanning component of strategic management. It is part of an external environment analysis when conducting a strategic analysis or doing market research, and gives an overview of the different macro-environmental factors to be taken into consideration. It is a strategic tool for understanding market growth or decline, business position, potential, and direction for operations.

- Political factors relate to how the government intervenes in the economy. Specifically, political factors have areas including tax policy, labor law, environmental law, trade restrictions, tariffs, and political stability. Political factors may also include goods and services that the government aims to provide or be provided (merit goods) and those that the government does not want to be provided (demerit goods or merit bads). Furthermore, governments have a high impact on the health, education, and infrastructure of a nation.
- Economic factors include economic growth, exchange rates, inflation rate, and interest rates. These factors can drastically affect how a business operates. For example, interest rates affect a firm’s cost of capital and therefore to what extent a business grows and expands.
- Social factors include cultural aspects and health consciousness, population growth rate, age distribution, career attitudes, and emphasis on safety. High trends in social factors affect the demand for a company’s products and how that company operates. For example, the aging population may imply a smaller and less willing workforce (thus increasing the cost of labor). Furthermore, companies may change various management strategies to adapt to social trends caused by this (such as recruiting older workers).
- Technological factors include technological aspects like R&D activity, automation, technology incentives, and the rate of technological change. These can determine barriers to entry, minimum efficient production level, and influence the outsourcing decisions. Furthermore, technological shifts would affect costs, and quality, and lead to innovation.
Marketing mix (4P)
4P or Marketing mix is a set of interrelated actions of a company aimed at gaining and retaining market share. The marketing mix can also be called a marketing plan.
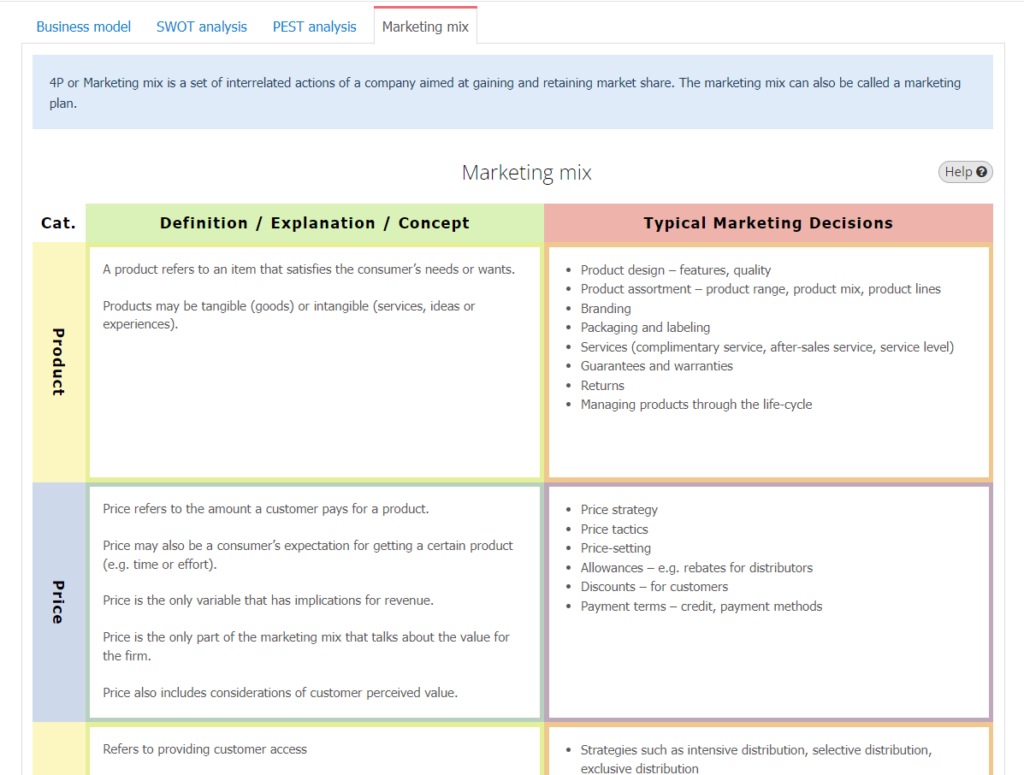
- Product. This represents an item or service designed to satisfy customer needs and wants. To effectively market a product or service, it’s important to identify what differentiates it from competing products or services. It’s also important to determine if other products or services can be marketed in conjunction with it.
- Price. The sale price of the product reflects what consumers are willing to pay for it. Marketing professionals need to consider costs related to research and development, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution—otherwise known as cost-based pricing. Pricing based primarily on consumers’ perceived quality or value is known as value-based pricing.
- Placement. When determining areas of distribution, it’s important to consider the type of product sold. Basic consumer products, such as paper goods, often are readily available in many stores. Premium consumer products, however, typically are available only in select stores.
- Promotion. Joint marketing campaigns are called a promotional mix. Activities might include advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, and public relations. One key consideration is the budget assigned to the marketing mix. Marketing professionals carefully construct a message that often incorporates details from the other three Ps when trying to reach their target audience. Determination of the best mediums to communicate the message and decisions about the frequency of the communication also are important.
 Business games
Business games  Бизнес игры
Бизнес игры  Juegos de negocios
Juegos de negocios  Geschäftsspiele
Geschäftsspiele  Jogos de negócios
Jogos de negócios  Giochi aziendali
Giochi aziendali  Jeux d'entreprise
Jeux d'entreprise  Trò chơi kinh doanh
Trò chơi kinh doanh  ألعاب الأعمال
ألعاب الأعمال  Επιχειρηματικά παιχνίδια
Επιχειρηματικά παιχνίδια  Forretningsspil
Forretningsspil  משחקי עסקים
משחקי עסקים  商业游戏
商业游戏  비즈니스 게임
비즈니스 게임  Permainan perniagaan
Permainan perniagaan  Zakelijke spellen
Zakelijke spellen  Forretningsspill
Forretningsspill  Gry biznesowe
Gry biznesowe  Jocuri de afaceri
Jocuri de afaceri  İş oyunları
İş oyunları  Liiketoimintapelit
Liiketoimintapelit  Obchodní hry
Obchodní hry  Affärsspel
Affärsspel  ビジネスゲーム
ビジネスゲーム