Managing stores in the simulation
An example of how the stores work is shown on your company’s homepage:
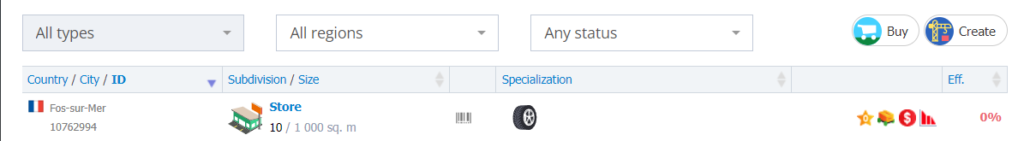
Click on “store” and you will receive the information on store’s location, type, and products.
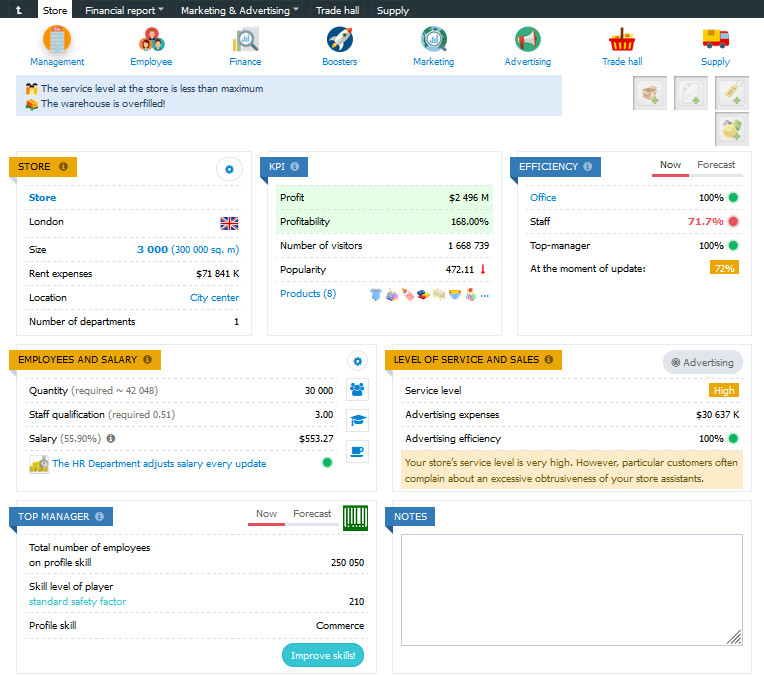
Price, quality, and brand
The business model of the store is quite simple: buying supplies (at a low price) and selling to end consumers (at a higher price). The price margin has to cover all the expenses (rent of the premises, salary, advertising expenses, etc.)
What is the most important?
What is more important: the price, quality, or brand? There is no straightforward answer to that question. For example, if you establish a network of jewelry stores in upscale areas of the city, in that case, the quality and the brand of goods will be very important. However, if your store is located in a residential area, an affordable price will be the key factor.
Do not be afraid to experiment with the prices, quality, and brands.
You can sell various kinds of products in one store. The list of products depends on the game intensity. There is a choice of 205 types of products in Classic format (with daily game turns) and 40 in Intensive (with hourly turns).
Each product has its price, quality, and brand. It depends on the type of product, location of the store, competitors, and other factors.
There are different types of prices in the simulation:
- Supplier’s price — the price of goods, excluding transportation expenses and customs duties.
- Purchase price — the price you are going to pay to the supplier, including transportation expenses and customs taxes.
- Selling price — the price you are going to set for end consumers.
- Average city price — the average price of a specific product in a specific city.
Quality —can be any number (starting from 1 as the lowest quality indicator). The higher the quality is, the better the product’s selling potential. Brand — the indicator of consumer appeal. The higher the brand is, the better the product’s selling potential.
Ordering supplies
To select the supplier, go to your store, click on the «Supply» tab, select the product category and specify the type of the product, then click on «Select supplier».
Important
The purchase price may differ considerably from the supplier price in case long-distance transportation is required.
When setting up the final price, you should consider such factors as the purchase price, the additional expenses as well as the average city price of the product.
In case there are two products of the same or almost the same quality, you should buy the one with a lower supply price.
If two products have the same or similar price, we buy the highest quality products.
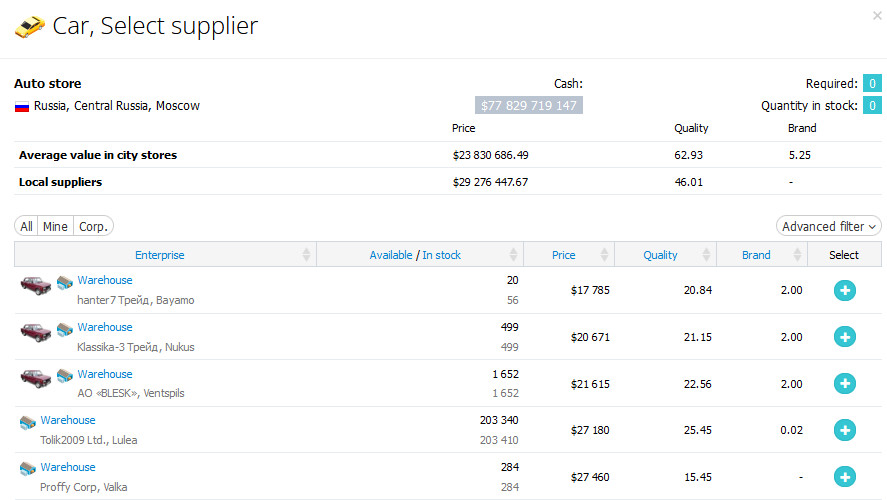
Select the supplier of your choice from the list. Click on «Select», enter the number of units you would like to purchase, and click on «Place an order». You will receive your order after the next game turn.
Things to consider
When signing a contract with a supplier, you can set specific conditions, like stopping the supply in case the price has increased by X%, or stopping the supply in case the product quality has decreased by Y.
All contracts are long-term by default. That is, if you order 100 units, every game turn you will receive precisely 100 items.
If you wish the contract to be valid only for one game turn, tick the “One-time purchase” box.
Price examples of Car supplies.
When you are in the process of selecting products for your store, it is crucial to know whether there is a market demand for these products. Otherwise, there is a risk of investing in a product that will not sell.
Market analysis and selling potential
To determine product selling potential, you need to conduct a thorough market analysis as well as a price and quality analysis.
You have established your store in a certain location (country, region, and city). To have a clear picture of the market situation, click on «Analytics» > «Market analysis» and select the product and the region.
An example of a market report on Tires in Moscow.
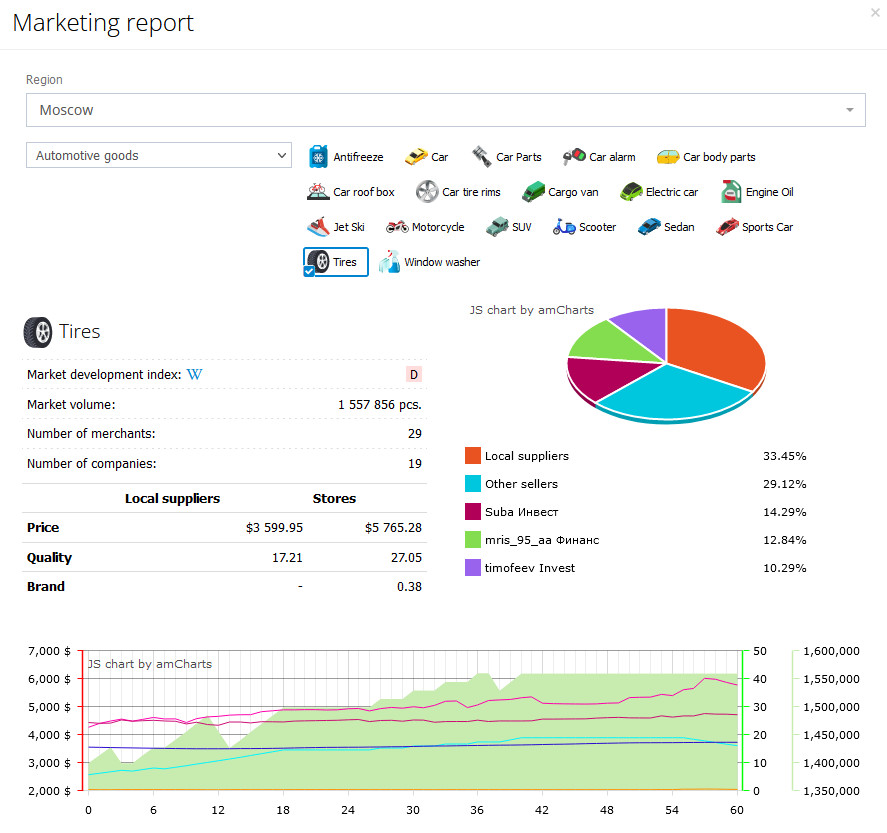
Understanding market analysis data
For quick assessment look at the market development index. If it has a value of “E”, it means there is a selling potential in such a market, since it is occupied only by local suppliers (computer-generated stores, which are relatively easy to compete with). If the development index is “AAA”, it means that there are real players in the market and it will be more difficult to compete. Notice the changes in price and quality. For example, the quality of this product in the market is minimal (1), the price has been decreasing since the last game turns and now it is a bit over 32.
Therefore, if you can find a supplier of sausages (or build a sausage factory yourself) with a quality equal to or bigger than 1, but at a lower price, you have an excellent chance to generate profit.
Take a look at the list of the biggest non-computer–generated buyers. They are good indicators of understanding the selling potential of specific products. For example, each game turns “Fedorov and the company” sells about 100 units of 1.05 quality products at the price of 35.99. Therefore, if your product has the same quality, but the price is slightly lower, you can expect to sell 100 units of sausages each game turn.
Experiment with the market
Try to apply various product ranges and price strategies. Experiment with supply and prices and adjust your strategy aftermarket reaction.
In some cases it is better to have a smaller margin (the difference between the selling price and the purchase price), but bigger sales volumes due to the offer of a favorable price / quality / brand combination.
Also, you can choose the strategy of bigger margins and smaller sales volumes.
The following example will help you have a better understanding of the selling potential based on the correlation between product price and quality.
Trade hall
When you order the supply, the information on the average city price and quality of the product, your supply and sales volumes, product volumes in stock, etc. can be found in the store’s trade hall. You can set the selling prices of your products in the trade hall of your store.
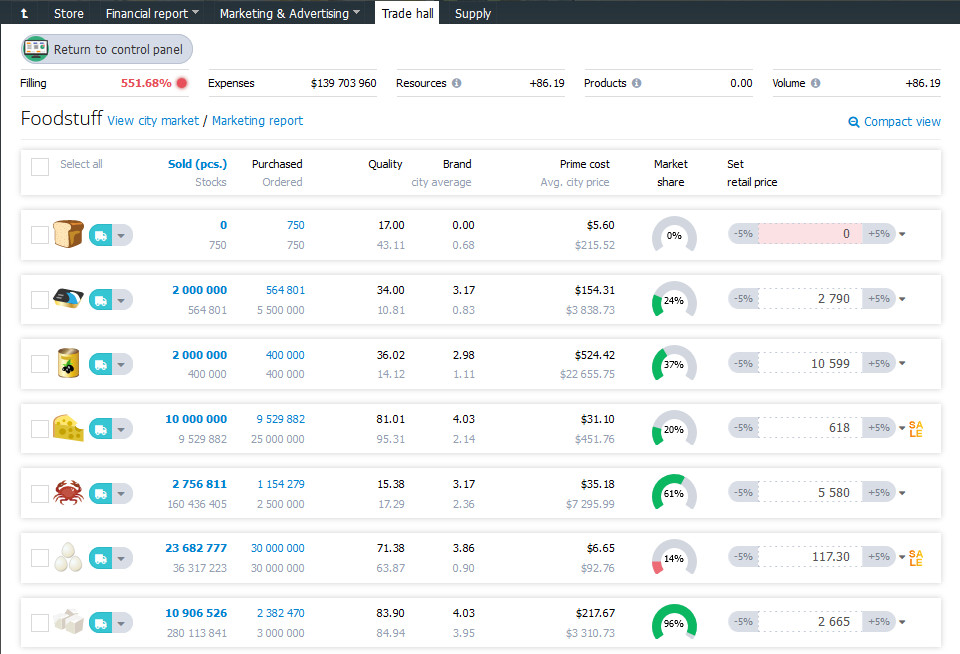
Market Analytics
Do not forget to refer to the analytics reports in the business simulation. They contain information on market structure, key competitors, and their prices, as well as information on new markets to enter.
Click on «Analytics» for analytics and reference information.
Store size and location
The location of the store is very important. The closer the store is to the city center, the more the quality and the brand of products becomes vital. The further the store is from the city center, the more the product price becomes important.
You can change the location and the size of your store by clicking on «Store location».
Experiment with the market
Experiment with different strategies when selecting the location of the store, product range, and price margins.
The closer the store is to the city center, the higher the rent expenses. But the selling potential is bigger. Especially if your product is of good quality and reasonable price.
As your business starts to grow, there will be a need to increase the size of the store: it will help you sell more products and serve a bigger number of customers. The sign that you need to expand the store will be obvious: you will have long queues of customers in front of your store (there will be a notification of that). It means that the store has substantial customer traffic, a good price and quality correlation, and qualified employees, but the store itself is too small to serve all customers, which means it is time to expand.
Employees and Salary
Naturally, the store cannot function without proper staff. You can manage the HR department of your store by clicking on «Employees and Salary» on the homepage of your store. There you also can find the hint on how many employees your store currently needs.
Set the number of employees and their salary, hire, dismiss, and train your staff.
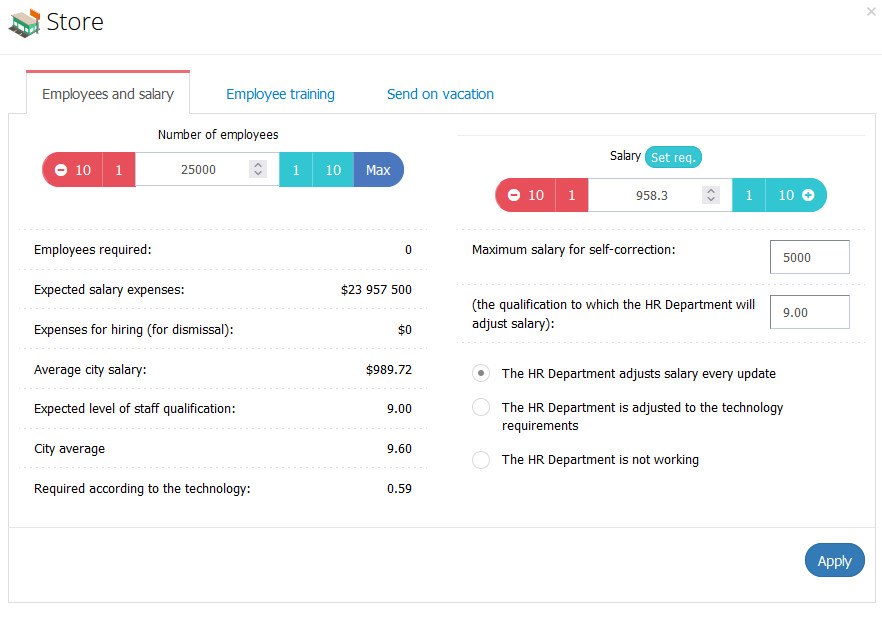
It is better not to save on your staff expenses and your employees are crucial to your business!
Here are some recommendations for HR management:
- Your employees should correspond to the size, specialization, and growth of your business. For example, if you spend a lot on advertising, make sure you have enough employees to service the increased customer traffic.
- To increase the sales volumes, a high level of service is required, which depends on employees’ skills. This factor is especially crucial for the stores, located in the city center or upscale areas.
- Sometimes it is better to decrease the unnecessary supply purchasing (which ties up your money) than save on your employees.
- It is always good to have some options. You can hire expensive yet qualified employees, or you can hire less qualified employees and invest in their training and development. Or you can opt for something in between these two strategies.
- Experiment with managing your HR department, it will help improve the overall efficiency of your staff.
Advertising
Advertising is crucial in attracting potential customers to your store. This eventually might translate into customer traffic and, consequently, bigger sales volumes. To set up the advertising campaign for your store, click on «Marketing and advertising».
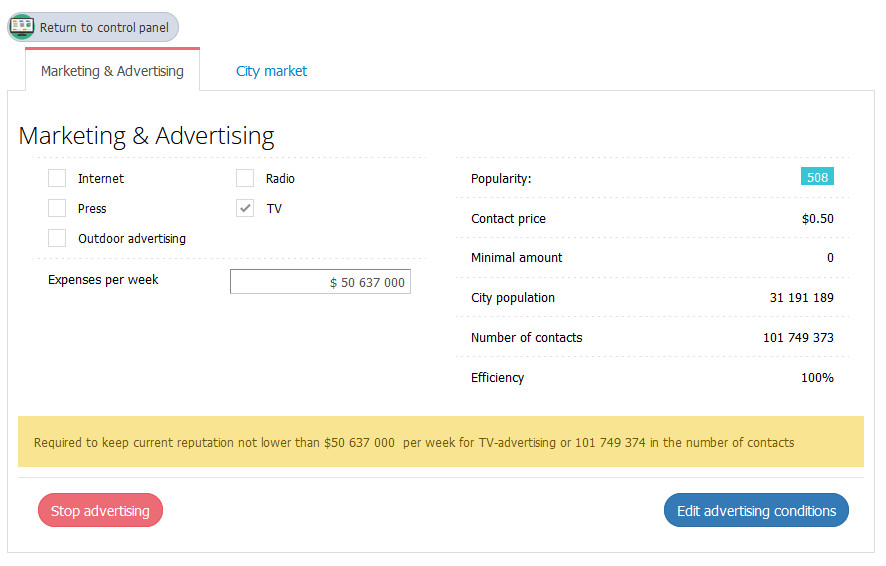
Try different advertising channels for maximum efficiency.
Advertising campaign efficiency
The more often potential customers see the advertising of your store, the better. Try to maintain a minimum contract figure to the city population ratio: not less than 2: 1 – 3: 1. That is, every resident of the city should see your ad at least 2-3 times.
Ideally, the advertising campaign of your store should be 100% efficient. The efficiency of advertising campaigns does not depend on how much money you have spent on it, but on how efficiently the customers were served in your store after they had seen your ad.
To achieve it, your store must work with 100% efficiency. This indicator is calculated regularly in the simulation (see. the homepage of your store). The low performance of your store means that not all visitors, who came to your store to buy something, were able to make a purchase.
The efficiency of the store depends on three factors:
- The efficiency of your employees (sales assistants): the number of people and their skills, that is, their ability to provide high-quality customer service.
- Manager’s qualification in Trade (you can see the information on your qualification in “My Company / Top Manager”.)
- The efficiency of your office.
The last two factors will be explained in detail in the following chapters.
Key metrics and business processes
STORE SIZE AND LOCATION

The size of the store largely determines the traffic of visitors. The larger the store, the greater the number of customers who enter the store simply “from the street” – this is the so-called basic traffic. In addition, the larger the store, the greater the influence of the store’s popularity on the growth of traffic – at the same level of popularity, a store with a larger size will attract a relatively large number of visitors (as a percentage of basic traffic). Given that the basic traffic to a larger store is also higher, the absolute increase due to popularity will be quite significant.
However, this does not mean that every time you open a store it should be of maximum size. A large store is highly demanding in terms of staff qualification, top manager skills, and volume of supplies. The ideal size of the store is sufficient to maintain a high level of service and store efficiency.
In addition, from the point of view of a buyer, the product offers in large stores are more passive. The smaller the store, the more visitors react to the appearance on the shelves of a truly good product. While in a large store, a visitor may simply not notice a profitable offer.
Location of the store, as well as its size, determines the basic traffic. Stores located in the City center have the maximum basic traffic. Next in descending order by traffic decrease: Residential area, Outskirts, Suburbs, and Trendy neighborhoods. The average level of wealth in a Residential area corresponds to the average level in a city. As you move from the center to the suburbs, the level of wealth gradually decreases. But in a Trendy neighborhood, the level of wealth can significantly exceed the average value of the city. Naturally, the number of buyers with such a high level of income is not very large. The closer the store is to the city center, the higher the purchasing power of visitors and the lower the elasticity of demand.
In addition to traffic and the level of wealth, as well as the buyers’ preferences (determined by the level of wealth), the location of the store can be significant in markets with strong competition. Specifically, in saturated markets, there is strong competition on the city district level. Accordingly, if most of the stores are located in the city center, then they will suffer primarily from a high level of competition. While a lonely store on the outskirts will not be affected by those major trade wars.
KPI
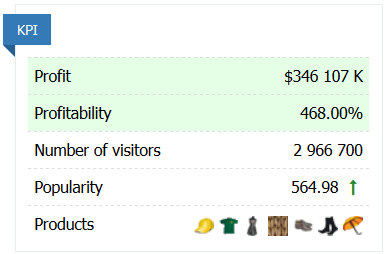
The number of departments in the store is determined by the number of product categories in the Trade hall. The fewer departments, the better, as given other equal conditions, each specific product is sold. In addition, with a higher number of departments, it is more difficult to maintain a high level of service. The total area of the store is divided equally into all departments. At the same time, it does not matter what the reserve (in a warehouse) of the goods presented in the Trade hall and how well they sell. Therefore, it is recommended to timely clean up the Trade Hall from “ballast”, for which the operations – “Move products to the warehouse” and the group operation “Eliminate the remaining goods” are provided in the Trade Hall.
The store’s popularity level determines the actual store traffic to the basic traffic. The higher the popularity value, the more visitors come to the store on average. The popularity of the store can be increased through advertising. The number of visitors that come to the store, depends on its popularity and the size of the store – the larger the store, the more curious visitors it attracts for each unit of the popularity value.
The store’s sales volume primarily depends on the number of visitors. The number of visitors, in turn, depends on the degree of popularity of the store. When a new store is opened, its level of popularity is zero and only random visitors from the street enter it. You can increase the popularity of the store through advertising. An advertising campaign can cost quite a lot of money, but the effect of increasing sales can significantly cover costs. Sometimes it makes sense to conduct a large-scale advertising campaign immediately after the opening, as this will ensure the initial popularity of the store and quickly make it profitable.
The efficiency of an advertising campaign of the store depends on the amount of money spent, as well as on the type of advertising and its efficiency. The more money you invest into advertising, the more large-scale channels you can use to attract the attention of the buyers: from the Internet and outdoor advertising to radio and television. It is necessary to ensure that the visitors of the store are provided with the necessary level of service, that is, the size of the retail space and the number of personnel correspond to the tasks of the store.
Over time the effect of promotions decreases, and the amount required to maintain the store’s current popularity increases. To maintain a constant level of fame for the store requires almost constant promotions.
The number of customers who come to the store is one of the key characteristics that determine the sales volume and, accordingly, the success of the trade. The more customers visit the store, the greater the sales. On the other hand, an excessive number of visitors can jeopardize the effectiveness of sellers and significantly reduce the level of service, which will not increase, but, on the contrary, reduce sales. The number of customers is determined by the number of residents in the city, the size of the store, and its location. This is the so-called basic traffic. The final number of buyers is calculated relative to the basic traffic, taking into account the effect of advertising, as well as a random factor (± 20%).
EFFICIENCY
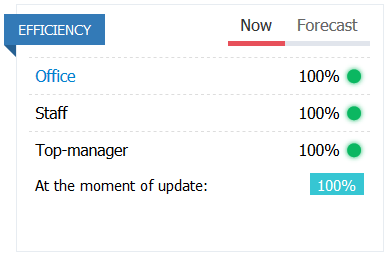
Efficiency of the Office – the efficiency of the managing office of the region, where the store is located.
The efficiency of the staff. The efficiency of the sellers determines how well the store staff copes with their duties and how well the visitors (who arrive) are served. The higher the number of store visitors and their wealth level, the more sellers are needed for their highly efficient work, and the higher their qualifications should be (the richer the customer, the more finicky he is). The effectiveness of sellers affects the overall performance of the store and the level of service in the store.
The efficiency of a top manager. Depends on the correspondence of the top manager’s skill (Trade) to the qualifications of the staff in all similar (use Trade skill) subdivisions of the company as a whole.
Efficiency – the efficiency of the store for the last turn. It is a function of 3 indicators of efficiency – staff, office, and top manager. Efficiency is a key parameter that determines the success of a store. Low efficiency negatively affects sales, regardless of product mix and level of service. The low efficiency of the store means that not all visitors who wanted to make purchases were able to do this. With a decrease in work efficiency by 30%, sales can be halved.
EMPLOYEES AND SALARY
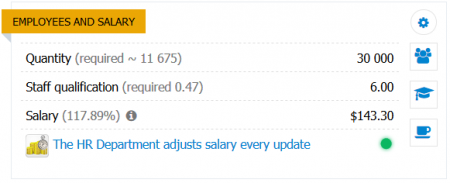
Quantity of employees – the current number of employees in the store. Determines the level of service. Additionally, the size of inventories affects the required number of employees. When the warehouse is overcrowded, the required number of employees increases, which can affect the drop in the level of service.
Salary of one employee – weekly salary of one employee. The average salary of employees of this type of unit in the city is indicated in brackets (each type of business unit has its coefficient).
Staff qualification – the current qualification level of employees (in addition, the average city qualification value and the required value determined by the quality of goods are indicated in brackets).
LEVEL OF SERVICE AND SALES
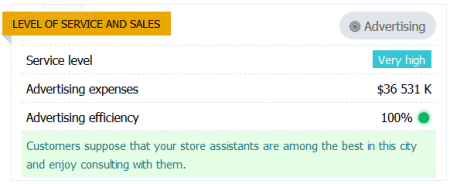
Level of service is an important characteristic of the store, which determines the quality of customer service. Ultimately, the higher the level of customer solvency, the more the level of service affects sales. For wealthy customers (for example, from Trendy neighborhoods), the level of service can be very important, more important than the price of goods. The level of service consists of two components: the sufficiency of retail space and the coordinated work of sellers. And, of course, it primarily depends on the number of visitors, since five people can easily fit in an area of 20 square meters, but 500 can hardly be accommodated. Lack of space, insufficient number of sellers and / or insufficient qualifications of sellers are the main reasons for the decline in the level of service. Since the total area of the store and sellers are evenly distributed across each product group, the level of service directly depends on the number of departments in the store.
Service includes a certain proportion of attention given to each buyer by sellers. The more visitors, the fewer sellers – the less attention each seller can give to customers. The store staff is also characterized by the level of qualification: the higher the qualification, the higher the level of service. Often, a small number of highly qualified sellers can serve visitors better than an army of low-skilled sellers.
However, one should not forget: if, in the pursuit of high service, the store owner hires too many sellers and / or the sellers are overqualified, then due to the insufficient skill “Commerce” of the store management of Top-manager, the overall efficiency of the store may drop sharply.
Another important detail: it is very difficult for huge developed supermarkets in large cities to provide an elite level of service. Therefore, a powerful advertising campaign will lead to an influx of visitors, and that will cause a catastrophic collapse in the level of service, as a result bringing the store more harm than good.
When evaluating the level of service, it is useful to pay attention to the staff efficiency. These characteristics perfectly complement each other. However, it should be remembered that when assessing effectiveness, the area factor and the number of product sections are not taken into account.
TOP MANAGER
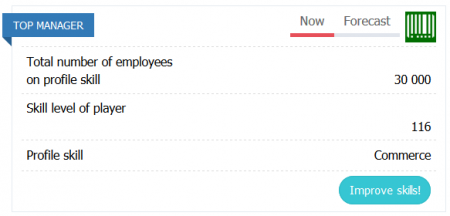
Total number of employees on profile skill is the total number of employees of all enterprises in this field in the company. It affects the effectiveness of the top manager.
Skill level of player – current “Commerce” skill level of the Top-manager. Determines maximum manageable number and qualification of personnel without loss of efficiency both in this particular unit and in all enterprises of the company as a whole (an additional hint about the reserve of the current level compared to the minimum requirements can be indicated in brackets, minimum – 0-25%, normal – 25-50%, good 50-100%, excellent more than 100%).
TRADE HALL
Trade hall reflects the current state of affairs in your store. It shows all the goods presented on the shelves of your store, as well as ordered goods and those which sale has already been discontinued. For each good, the column “Sales volume” indicates sales for the last week (turn), and the link below this value leads to statistics on sales of goods for the last 52 weeks (indicating the number of goods, quality, brand, and selling price for each week).
The following columns contain information about the current supply of the store with this type of product. “Purchase volume” – current order / actual purchase for the last week (in brackets). Information about the current stock of products – “In stock”, “Quality”, “Brand” and “Purchasing price” of products. “Market share” of your store of a specific product in the whole city, and the average city statistics for the same good (including both Local suppliers and all existing player stores).
To start sales in the store, you must have goods on the shelves of the Trading Hall and be sure to set the price and type of sale on it. By default, the type of sale is set to “Regular sale”, in which the store operates in standard mode and sells goods at the prices set by the manager (you). Please note that if you do not set a price (leave 0.00), it will be equivalent to setting the type “Do not sell” and there will be no sales of the specified product. In the “Sale” mode, the system automatically selects a price based on conditions to maximize sales. At the same time, the price is not influenced by the cost of the goods or by the price set by the manager (you). At the same time, under the price-setting window, the inscription “sale” appears and in the window itself the price, at which the goods were sold in the last turn, is displayed.
Under the window to choose the type of sale, there is a form for simplified choice of supplier of goods and a block of special operations to eliminate the remaining goods. If you want to close the department, then you need to check the boxes next to ALL products from the department and click “Eliminate remaining goods”. Moreover, all inventories will be eliminated without any compensation. However, be careful: this function does not interrupt orders for these types of goods, so if you do not stop the supply orders for these items, the department may reappear when purchasing at least one unit of any product from the category of the department.
SUPPLY
Supply tab displays all contracts for the purchase of products in your store. You have the opportunity to adjust existing contracts:
- change the number of products purchased,
- set limits on the contract for cancellation if – there is a certain relative or absolute change in price or there is a decrease in the quality of delivered goods below a certain threshold),
- and enter new contracts for the supply of any product present in the game.
Above the list of contracts, the preliminary value of the order is calculated at current prices (at the declared quantity and affordable prices), as well as the sum spent for purchase for the previous turn. This will allow you to plan the company’s budget for the current turn.
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF RETAIL TRADE
Local Suppliers
In Virtonomics players have to compete not only with other players but also with local suppliers. These retail enterprises represent a mass of various stores in the city and originally they are in full control of the retail market.
Each retail product in every city has an average price and average quality, mostly typical for local suppliers. This means that this product is sold by local suppliers for this certain price and with this certain quality in this specific city, if there are no enterprises created by players.
In most cases, to compete with local suppliers successfully you must offer goods of higher quality at lower prices. Terms of local suppliers always change as a market of a certain good grows, local suppliers decrease their price and improve quality, and competition in this sector becomes more severe.
Preferences of Customers
Wealth Level is the most important factor in defining customer preferences. In cities with low wealth levels people spend almost all their money on most needed goods, and they have no big interest in luxury goods. They pay special attention to the price as they prefer buying cheaper products instead of famous and high-quality goods.
While, in cities with higher wealth levels people can afford to buy household equipment, cars, and jewelry. In their opinion, high quality is more important than low price. Wealthy customers first of all require good service.
Customer’s preferences often change in favor of one or other goods. For example, sudden growth in a certain city in household electronics sales can be observed, but one virtual year later this sector can come to complete stagnation, while customers will start to buy furniture and jewelry. These changes can often be unpredictable however marketing research can reveal consumer trends.
Competition and Market Saturation
There are two kinds of retail markets in Virtonomics: saturated and unsaturated. A segment of local suppliers in saturated markets is always zero.
In an unsaturated market, all sales are determined by the attractiveness of supply (combination of price, quality, and brand).
Redistribution of sales in saturated markets has two stages: competitive and proportional. During the competitive stage sales volume depends on the attractiveness of the offer, and during the proportional stage all stores are equal. The percentage of each stage depends on the city and the goods: for high-developed cities (and for luxury goods) competition is more significant.
There are three basic stages of market saturation:
- The first stage (saturation): minimal competition, fixed market volume, and «excessive» sales are removed (due to smooth proportional bringing the specific number of purchases (see Trade in saturated markets) to the standards of saturated market).
- The second stage (stretching): all stores work with restrictions, and the market volume is smoothly increasing.
- Third stage (over-saturation): market volume is unstable (it can drop down to the basic volume, but in general it tends to move towards the maximum stretching of the market), competitive and proportional penalties for «excessive» sales, including district competition.
Trade in Saturated Markets
Stores will compete with each other depending on their location. It means that stores located in a district with a high concentration of stores will have a bigger penalty. The system will calculate how much goods would have been sold by all these stores and after this sales volume for certain stores will be decreased. It is not the number of stores in the important area, but their total sales, i.e. one store measuring 100 000 m2 can have a greater impact than 10 small stores.
Uniqueness
This parameter is valid only for one company and in only one city. It expresses the conformity of your goods. Stores of your competitors and your stores in one city do not influence the uniqueness of stores in other cities.
Two parameters are important in defining the uniqueness: variety of goods and conformity of assortment. The manufacturer of goods in one store will be compared to the manufacturer of goods in another store and in case if they are the same — you will have to pay a penalty for non-uniqueness. For instance, 3 stores with identical assortment produced by the same manufacturer will have 50% uniqueness. Penalty will be applied only for the third store and up: it is possible to have two identical stores in one city but if you have more than two their uniqueness will go down. If the number of such stores will increase, uniqueness will fall further. As a result, the turnover of 10 completely identical stores will be only 4 times more than one.
Please also take into consideration:
- There is no division for separate subdivisions. For example, a company produces goods at the enterprises E1 and E2. Goods from E1 go to Store 1 and goods from E2 goes to Store 2. As a result, these two stores won’t be unique.
- Agent companies won’t influence the manufacturer of the goods. For example, Company A produces goods. Company B buys it. After this company C buys it from the warehouse of company B and supplies it to its own store. As a result, company C will sell goods, produced by company A.
- Variety of assortment. If the products in different stores are not completely identical (one store sells cars, the second store sells cars and motorcycles, and the third store sells cars and tires) this will produce a positive effect on the uniqueness, and the penalty will not be so big. Sales volume is not important, only the availability of goods is significant. If you want to add new goods to improve the uniqueness, don’t forget that stores with one single department have better sales.
- Products of similar quality and brands produced by different manufacturers are considered to be unique (no penalty). If you sell mixed goods from two manufacturers their uniqueness will be evaluated separately.
About restrictions per visitor. One buyer of a unique store with one product section can buy, for example, clothes:
- 100 m. | 50 units.
- 500 m. | 10 units.
- 1000 m. | 4 units.
- 10 000 m. | 1-2 units.
- 100 000 m. | ~0.6 unit.
These are approximate values only for the reference. 50 units refers to the goods of highest quality and brand sold in the store with the best service level. In this situation the store plays a role of a super-popular boutique which has few very rich customers. In case with unsaturated markets this value can be much higher especially for big stores.
 Business games
Business games  Бизнес игры
Бизнес игры  Juegos de negocios
Juegos de negocios  Geschäftsspiele
Geschäftsspiele  Jogos de negócios
Jogos de negócios  Giochi aziendali
Giochi aziendali  Jeux d'entreprise
Jeux d'entreprise  Trò chơi kinh doanh
Trò chơi kinh doanh  ألعاب الأعمال
ألعاب الأعمال  Επιχειρηματικά παιχνίδια
Επιχειρηματικά παιχνίδια  Forretningsspil
Forretningsspil  משחקי עסקים
משחקי עסקים  商业游戏
商业游戏  비즈니스 게임
비즈니스 게임  Permainan perniagaan
Permainan perniagaan  Zakelijke spellen
Zakelijke spellen  Forretningsspill
Forretningsspill  Gry biznesowe
Gry biznesowe  Jocuri de afaceri
Jocuri de afaceri  İş oyunları
İş oyunları  Liiketoimintapelit
Liiketoimintapelit  Obchodní hry
Obchodní hry  Affärsspel
Affärsspel  ビジネスゲーム
ビジネスゲーム